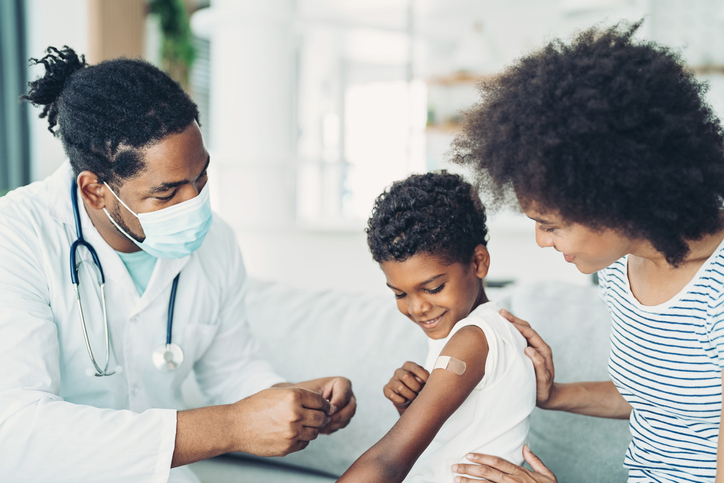
 Are children with a history of MIS-C at greater risk of severe reaction from COVID-19 vaccine?
Are children with a history of MIS-C at greater risk of severe reaction from COVID-19 vaccine?Common adverse reactions included arm soreness, fatigue, and fever, but no serious adverse events, such as recurrent MIS-C or myocarditis, were reported. Enterprise Analytics Core domain(s): Vaccines, COVID-19, community health, policy guidance Summary Key takeaways *Carelon Research associate at the time of the study.
Background
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is a rare, severe inflammatory response that occurs a few weeks after a COVID-19 infection. COVID-19 vaccines have been shown to decrease the risk of severe infection and complications. However, safety data from children receiving the COVID-19 vaccine after infection and MIS-C complications are limited. It is unclear if children who experienced MIS-C are at risk of a similar immune response after a COVID-19 vaccine. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recommends delaying vaccination until at least 90 days after the MIS-C diagnosis.
Objective
This study aimed to describe adverse reactions following the COVID-19 vaccine in children who had MIS-C.
Methods
In early 2022, as part of the NIH/NHLBI sponsored observational study named Long-Term Outcomes After the Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MUSIC), investigators from Carelon Research worked with MUSIC study sites to contact eligible participants. MUSIC participants 5 years of age or older with at least 90 days since their MIS-C diagnosis were contacted and asked to complete a questionnaire about their COVID-19 vaccination status and adverse reactions.
Results
Roughly 48 percent of eligible study participants received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine. This is comparable to national vaccination data. Common adverse reactions included arm soreness, fatigue, and fever, but no serious adverse events, such as recurrent MIS-C or myocarditis, were reported (Figure 1).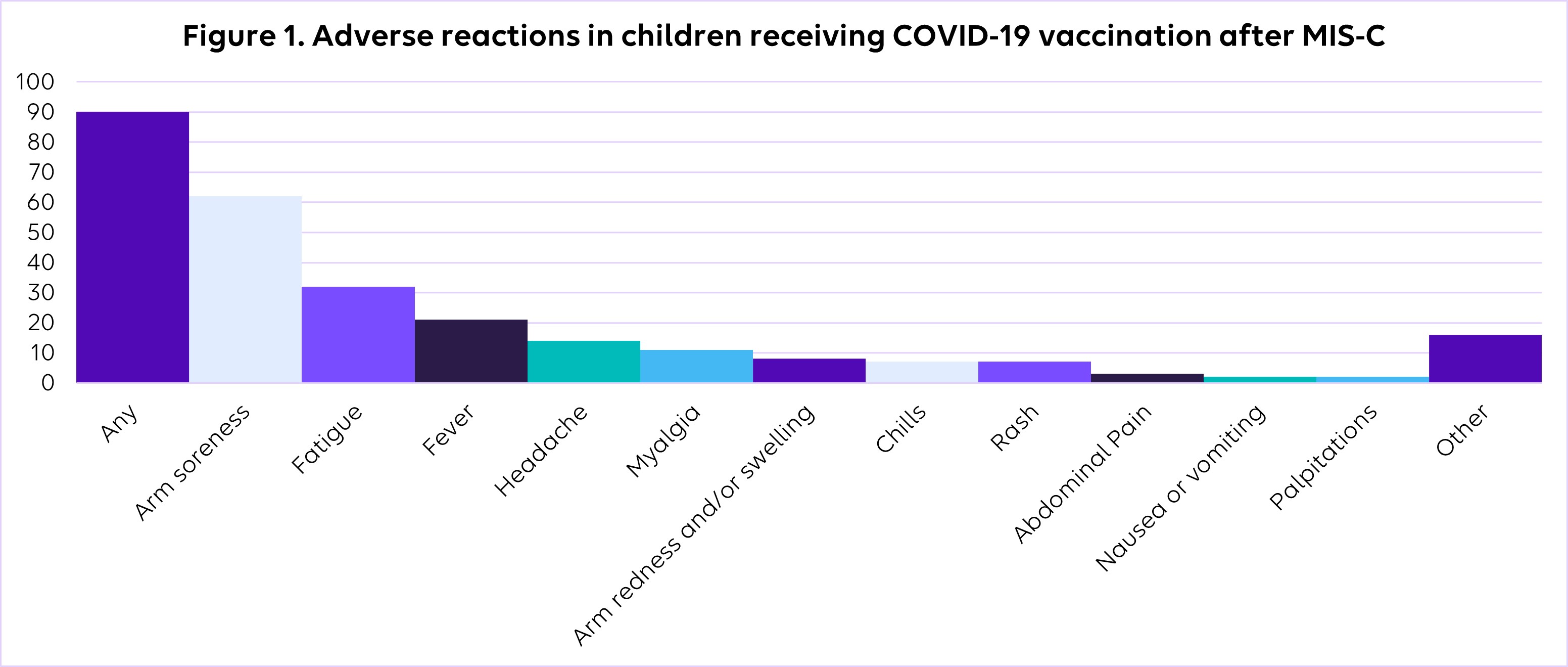
Compared to the general population, the COVID-19 vaccine appears to be safe with similar side effects for people who had an MIS-C infection, as long as the vaccine is administered at least 90 days following MIS-C diagnosis.
Publication(s)
Carelon Research project team: Felicia Trachtenberg, Xiangyu Mu*
For more information on a specific study or to connect with the Actionable Insights Committee,
contact us at [email protected].This study was conducted by the Pediatric Heart Network, for which Carelon Research, Inc., a subsidiary of Elevance Health, serves as the Data Coordinating Center. This study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dissemination and sharing of the Newsletter is limited to Elevance Health and its subsidiaries and included findings and implications are for Elevance Health and its affiliates’ internal use only.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut.

Adherence to COPD regimen resulted in an estimated average saving of $141 per patient per month in total costs in addition to improved survival and lower risk of hospitalization.

Death data from a combination of sources including Elevance Health may prove to be a reliable source for advancing our research and understanding of treatments and mortality.

Findings suggest deductible levels have little impact on breast cancer care during two years following diagnosis.

"Et harum quidem rerum facilis est et expedita distinctio!"

"Nam libero tempore, cum soluta nobis est eligendi."

"Temporibus autem quibusdam et aut officiis debitis!"